Upper GI Series
Upper Gastrointestinal Series also called Upper Gastrointestinal Studies or Barium X-rays of the upper gastrointestinal tract are medical radiography diagnostic tools used to examine the upper gastrointestinal tract for abnormalities.The upper GI series is used to examine the esophagus, stomach and duodenum.
For this test, the patient drinks a contrast solution that contains barium. arium sulfate mixed with water is ingested or instilled into the gastrointestinal tract and standard X-rays are made of the regions under examination. Because Barium is an X-ray contrast medium, it enhances the visibility of the relevant parts of the gastrointestinal tract by coating the inside wall of the tract and appearing white on X-ray film. This in combination with standard X-rays allows for the imaging of parts of the upper gastrointestinal tract such as the pharynx, larynx, esophagus, stomach, and duodenum such that the inside wall lining, size, shape, contour, and patency are visible to the examiner.
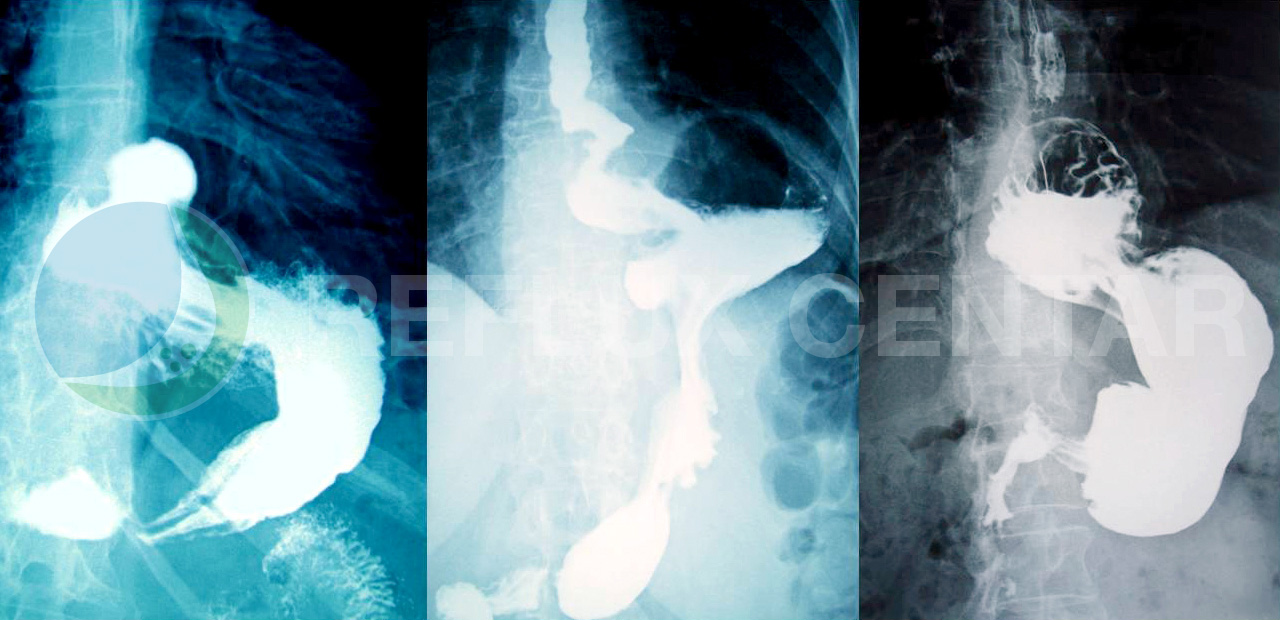
In combination with fluoroscopy it is also possible to visualize the functional movement of examined organs such as swallowing, peristaltic or sphincter closure. To further enhance the quality of images, air or gas is sometimes introduced into the gastrointestinal tract in addition to Barium and this procedure is called double contrast imaging. In this case the gas is referred to as the negative contrast medium.
The barium solution is sweetened and flavored, but does taste chalky.There will be both thick and thin mixtures of the barium solution you’ll be asked to drink (usually totaling 200 ml). The doctor or assistant will tell you when to take sips of the solution.
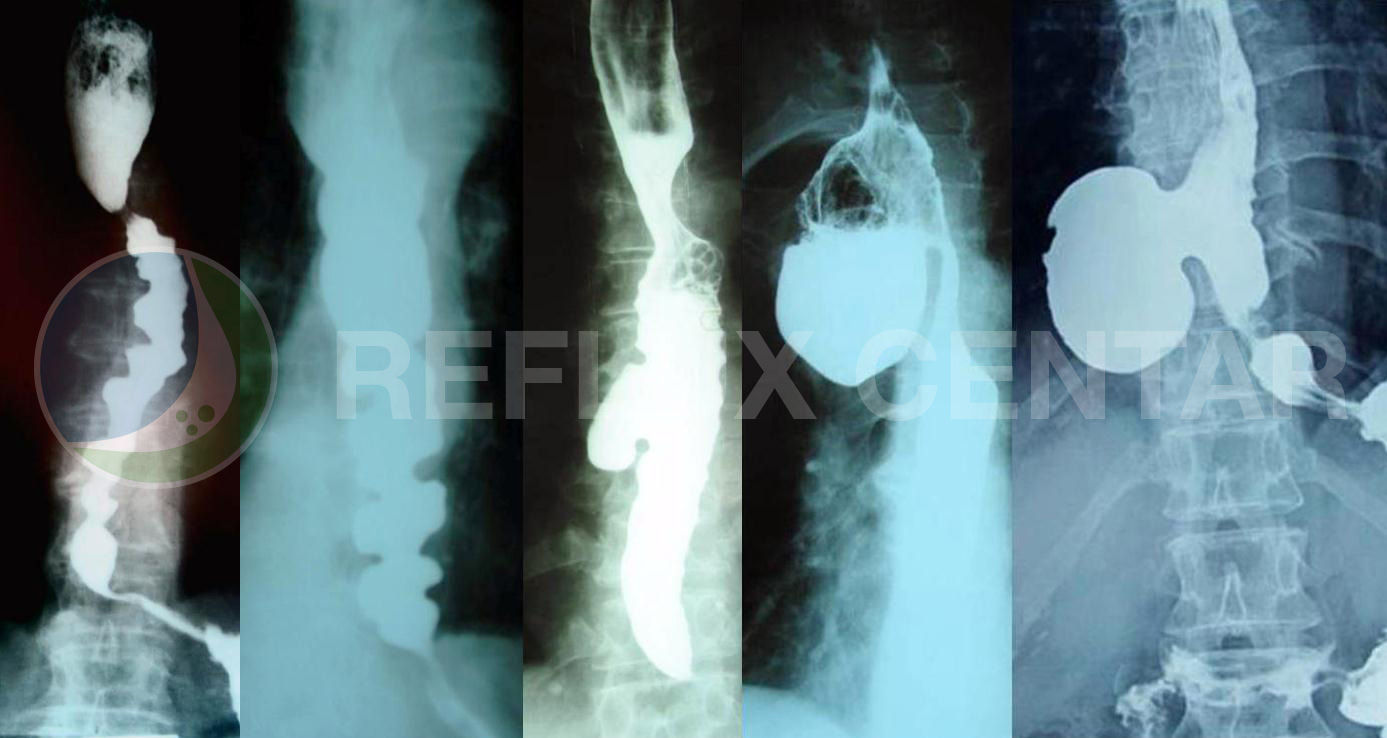
As the barium passes through the digestive tract, it provides an outline of the swallowing process as well as the esophagus, stomach and duodenum. The fluoroscope is held over the part of the body being examined and transmits continuous images to the video monitor.
This test is used to diagnose hiatal hernias, ulcers, tumors, diverticulitis, esophageal varices, obstruction, narrowing, or enteritis (inflammation of the small intestine lining). It may also be used to determine the causes of swallowing problems, reflux, abdominal pain, diarrhea, unexplained vomiting or weight loss or bleeding.
Diagnostics
- Medical History
- Abdominal Ultrasound
- Upper GI Series
- Upper GI Endoscopy
- Esophageal Manometry
- Esophageal 24-Hour pH Metry
- Esophageal 24-Hour pH Impedance
Lexicon
Patients Informations
Soon
If you have more questions contact us:
info@refluxcentar.com

 српски
српски
