Esophageal Diverticula
Esophageal diverticulum is defined as baggy extension through a weakened part of the esophageal muscular wall and can occur in all segments of the foregut, from the pharynx downwards to the stomach. Esophageal diverticula are classified depending on their localization:
1. Zenker’s diverticulum, the most common localized in the neck, just above the esophagus
2. Mediotoracal, in the middle of the chest
3. Epiphrenic, just above the diaphragm
Diverticula of the esophagus can occur in all ages of life, although they are more common in middle-aged or elderly patients. These diverticula are quite rare and are diagnosed in only 1% of upper GI series with less than 5% of patients who complain of feeling difficulty swallowing.
Details on the types of diverticula of the esophagus, as well as their symptoms and diagnosis, read below.
Diveretikulum represents baggy extension that protrudes from the lumen of the esophagus or any part of the digestive apparatus.Diverticulum of the esophagus to the material parts of the real (if extended all the layers of the esophagus, mucous membranes, submucosal tissue, muscle and adventitia) and false or pseudodivertikulume (when they contain only mucosa and submucosal tissue).According to the cause of divertikulmi esophagus can be divided into congenital and acquired.Depending on the mechanism of divertiukulumi can be pulzioni tractional.Pulzioni occur as a result of increased pressure within the body and spread to the wall of the city weakest material musculature.Traction occur due to adhesions which start from the outer wall of the esophagus to the adjacent organs esophagus pulling outwards.
Pulsion diverticula
Pulzioni diverticulum pharynx (hypopharynx) and esophagus are pseudodivertikulume in which the mucosa and submucosal layer pass through the muscle making baggy enlargement.Histopathological basis is being pulzionih diverticulum is always hypertensive, the upper or the lower esophageal sphincter and their inadequate coordination of relaxation during the act of swallowing.Although rare, squamous cell carcinoma can occur in approximately 0.5% of patients with a diverticulum.It is believed that cancers are due to a diverticulum chronic irritation diverikuluma present food.
Although rare, squamous cell carcinoma can develop in 0.5 percent of those with diverticula.This is thought to be caused by chronic irritation of the diverticula by prolonged food retention.
Zenker’s diverticulum

Zenker’s diverticulum represents diverticular expansion of the submucosal and mucosal tissue in the area of the rear wall of the pharynx or hypopharynx (Killian’s triangle).Zenker’s diverticulum forms due to the appearance of high pressure in the hypopharynx, which is a consequence of disturbances between the act of swallowing and relaxation UES.The eponym of the disease has emerged as the German doctor Friedrich Albert von Zenker (1825-1898) described 34 such cases.It occurs in about 0.1% of the 20,000 upper GI series of the esophagus.
The main clinical symptoms of Zenker’s diverticulum have difficulty swallowing the neck, associated with spontaneous return of undigested food.Chronic aspiration and frequent respiratory infections are common accompanying signs.When diverticulum increases significantly, descends through the space in front of the spinal column and can press the esophagus leading to almost complete obstruction of the lumen or the appearance of extreme difficulty swallowing until the impossibility of taking food and liquids (afagija).In almost all patients present and expressed bad breath (fetor ex-ore) due to the existence of decomposed food ingredients in a diverticulum.
Diagnosis is made by barium enema radiography and endoscopy.Endoscopic be two openings of the esophagus, one real and the other representing the lumen of the diverticulum in which one can find a greater amount of undigested food.Endoscopic examination must be done extremely carefully, because of the great features of the perforations divertikularnog enlargement.Manometry revealed hypertension and weakened or impaired relaxation of the upper clamp jednajka.
Treatment is exclusively surgical.Through the left oblique incision in the neck (cervicotomy) is made myotomy GES (krikofaringealnog muscle) and muscle layer of the pharynx and esophagus vrtanog work, a distance of about 6 cm.For small diverticulum (For larger diverticula (> 3 cm) recommended that after myotomy ways of cutting diverticula (diverticulectomy).In some cases it is possible to make and transoral endoscopic divertikulektomiju with special endoscopic stapler.
Epiphrenic diverticulum
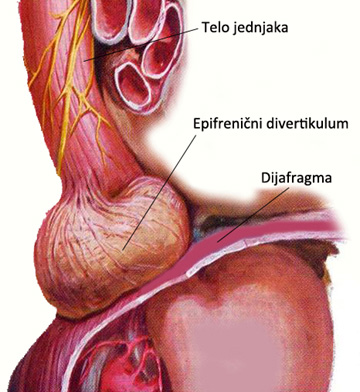
Epiphrenic or supradiafragmal diverticula occur on the body of the esophagus most often in the last 10 cm, and are pulsion diverticula that result from motor disorders of the body is equal to or functional obstruction at the level of DES.The predominant motor disorder is diffuse spasm, while in functional obstruction usually done on patients primarily suffering from achalasia.As with faringoezofagealnog diverticula, abnormal intraluminal pressure is responsible for prolapse of the mucosa and submucosa through the muscle layer.
The clinical picture is dominated by dysphagia and regurgitation and retrosternal pain mostly due to the joint nutcracker esophagus.Many patients are asymptomatic diverticula and accidentally reveal the barijumskoj radiography made one other reasons.Symptoms of existence epifreničnog dievrtikuluma is difficult to distinguish as a diffuse esophageal spasm, achalasia, esophageal hiatal hernia or reflux esophagitis.Diveritikuluma size varies from small to extremely large, which can even move only the body of the esophagus and lead to extreme dysphagia.And in these patients is present halitosis but it is less pronounced than that of Zenker’s diverticulum.The diagnosis is classically sets radiography Esophageal barium and endoscopy.Esophageal manometry is determined by a motor disorder of the esophagus as well as the functionality of DES.
Patients with less severe or no ikakavih symptoms generally do not require any treatment.On the other hand, patients with pronounced progressive dysphagia and chest pain or diverticulum, which increases, are candidates for surgical intervention.Through the left thoracotomy or laparoscopically, through the abdomen, ways to diverticulum resection (diverticulectomy), and then long esktramukozna ezofagomiotomija as in patients with achalasia.In case of hiatal hernia or inkompetentnog DES is necessary to make the antireflux procedure.
Traction diverticula
Traction diverticula are usually localized in the thoracic esophagus and are the consequence of pre-curing mediastinal granulomatous disease (tuberculosis or histoplasmosis).In this case it comes to real diverticulum, when due zapajenja in nearby lymph nodes leads to withdrawal – retraction of the entire body of the esophagus (not only mucosa and submucosa).In this way, a cylindrical shape formed of the diverticulum.These types of diverticula is mostly accidental diagnose because symptoms rarely given.Traction diverticula do not require any form of treatment.
Diseases
- Anatomy and Physiology of the Foregut
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
- Barrett’s Esophagus
- Hiatal Hernias
- Achalasia
- Esophageal Motility Disorders
- Esophageal Diverticula
- Helicobacter pylori gastritis
- Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD)
- Gallstones (Cholelithiasis)
Lexicon
Patients Informations
Soon
If you have more questions contact us:
info@refluxcentar.com

 српски
српски

